 Click To Return To Main Page |
 |
||||||||
 News |
 Eco-Journalists |
 Articles |
 Games |
 Links |
 Facts 'n Fun |
 Email Us |
 About Us |
 Guestbook |
|
|
Anna Burns has sent us in this great report on the environmental challenges faced by the African Savannah
Here's a bit about Anna: Name: Anna Burns School: Curtain Primary School Year or age: 11yrs old and Iím in year 5 Favourite animal: Donít have one, but horses and dogs are the closest Favourite music: Just about anything other than heavy rap Interests and hobbies: Piano, flute, taekwon-do and looking after my dog What would you change if you ran the world? A million things but to settle on one subject do something about global warming and ban whaling. The African Savanna
The savanna biome (also known as a plain) is grassland with some isolated trees and shrubs scattered through it. This biome is often near forest or semi-desert country. These are two pictures of the savanna:  
LOCATION The countries where you can find savannas include: about half of Africa, parts of India, China, Australia and South America, as shown by the map below. In this case we are focusing on the African savanna. 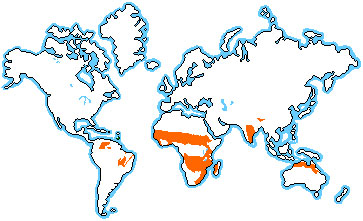
Africa has savannas on both sides of the Equator. They are bordered by the Sahara Desert to the North, and the Kalahari Desert to the South. Countries in the region include: Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Cote DíIvoire, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia, The Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Botswana and South Africa. Within these countries there are many towns and each has its own capital city. As you can see the savanna is not a small biome. CLIMATE The savanna climate has fascinated many scientists and students by the way it changes and by the secrets it holds. The savanna has a Monsoonal wet season (summer) with some twenty-five inches of rain per month from the beginning of May and ending in November, and a dry season (winter) between October and March (in the Southern Hemisphere) and April to September (in the Northern Hemisphere) when there is only four inches of rain. All this makes the African savanna a tropical biome, as shown immediately below.  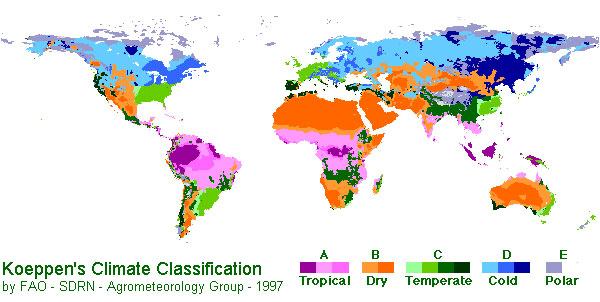
SOIL The savanna has rich volcanic soil which provides the plants with nutrition and the plants in turn provide the animals with food and shelter. Thatís where we come to the food chain. 
AFRICAN ANIMALS Africa has many species of plants and animals. Here are the animals that are alive today,
EXTINCT AND ENDANGERED ANIMALS OF THE AFRICAN SAVANNA. Extinct and endangered animals of the savannas. Key: C.D = Conservation dependent
*Tigers: Some people believe that tigers lived in Africa; others argue against that. These are just some of the extinct or endangered animals of the savanna. As you can see most of the animals hunted are carnivores and nearly all of them are hunted for their skins. The elephants however are hunted for their tusks, because of the money that is made. The white lion is hardly heard of because itís so rare otherwise the lions are at a lower risk. MEDICINAL PLANTS AND ANIMALS The medicinal plants and animals are used in medicine which helps people recover from illnesses. Unfortunately some of these plants and animals are endangered. Listed below are some of the medicinal animals and plants.
Many of these animals and plants are used for traditional medicines. Unfortunately some of them are endangered. HUMAN OCCUPATION Humans have made the African savanna their home, by building their factories, mines, houses and farms there. All of these have greatly affected the environment. Ever since the European settlers came to Africa the human population has increased by hundreds and the animalís population has decreased by thousands. The human population varies as the savanna climate changes each year. The rough population spread is: ranging from two to over 100 people per square mile and roughly 45% live in urban centres, otherwise population figures are hard to come by when looking at the savanna. Humans have mined many things in the savanna. Some of these things are: salt, coal, and some oil wells are also near by. When these things are dug up they are than transported over to other countries like: Australia, Asia, Europe, North and South America. The goods are also transported around Africa. Humans have introduced animals that have affected other animals. Cattle have taken territory away from the wild animals and they have also taken away the grazing plains for the other animals that feed on grass. As you can see human occupation has had a huge impact. PROBLEMS AND POLLUTION IN THE SAVANNA  Over the years humans have hunted many African animals to extinction, or close to it. Many of these animals are not mentioned in websites or books mainly because they havenít been discovered yet. Pollution is one of the main threats to Africaís savannas. The air can be polluted by smoke and exhaust fumes. If the air does get polluted animals will find it increasingly hard to breath and since they canít move out of the country they will eventually die out. Carbon dioxide (CO2) increases the heat of the biome, if too much carbon dioxide gets into the air the animals that have adapted to the plains may have to adapt again to fit into an almost desert-like biome. Seasons may have something to do with the savannasí fate. What if the seasons change their routine? What will happen to the savanna if they do? Well, if the seasons change their routine (by coming earlier or later than expected e.g. summer comes two months earlier) animals that hibernate in the winter will expect the wet season to arrive in June and may die out if the season arrives any earlier or later as their food would have gone back into hibernation (or may have already died out). Water is one of the most needed things in the world. Again most of the water that is in the savanna today contains many chemicals, as it has been through polluted areas with starving people and large factories. All animals have to have water. If the water is polluted the chemicals will pollute the animalís body and then the animal will die out. The food chain has a lot to do with this. If you take out the dung beetle you will have a lot of dung around and the animals could die from diseases. Right now there are some of these things happening and there is a possibility that these horrible things could happen. The dams hold in the germs and so when the waters released it carries the germs down through the country and into the bodies of the animals. Now the animals are being hunted and the water is being polluted. However there are people who try to preserve this ecosystem and its animals.
Over the years humans have hunted many African animals to extinction, or close to it. Many of these animals are not mentioned in websites or books mainly because they havenít been discovered yet. Pollution is one of the main threats to Africaís savannas. The air can be polluted by smoke and exhaust fumes. If the air does get polluted animals will find it increasingly hard to breath and since they canít move out of the country they will eventually die out. Carbon dioxide (CO2) increases the heat of the biome, if too much carbon dioxide gets into the air the animals that have adapted to the plains may have to adapt again to fit into an almost desert-like biome. Seasons may have something to do with the savannasí fate. What if the seasons change their routine? What will happen to the savanna if they do? Well, if the seasons change their routine (by coming earlier or later than expected e.g. summer comes two months earlier) animals that hibernate in the winter will expect the wet season to arrive in June and may die out if the season arrives any earlier or later as their food would have gone back into hibernation (or may have already died out). Water is one of the most needed things in the world. Again most of the water that is in the savanna today contains many chemicals, as it has been through polluted areas with starving people and large factories. All animals have to have water. If the water is polluted the chemicals will pollute the animalís body and then the animal will die out. The food chain has a lot to do with this. If you take out the dung beetle you will have a lot of dung around and the animals could die from diseases. Right now there are some of these things happening and there is a possibility that these horrible things could happen. The dams hold in the germs and so when the waters released it carries the germs down through the country and into the bodies of the animals. Now the animals are being hunted and the water is being polluted. However there are people who try to preserve this ecosystem and its animals.
WILDLIFE PARKS Here are some wildlife parks and they help the environment by trying to keep the plants growing, the rivers clean and the food chain balanced: 1. Eco travel Africa wildlife parks 2. African Safaris 3. Sabona wildlife reserve 4. Kakadu National park 5. Zambia- The real Africa CONCLUSION The conclusion is that this ecosystem is delicate and it needs to be kept in balance. Although some people try to conserve the environment and the animals in it, the main thing thatís happening here is global warming. This problem is not helped locally by some mining, but the main problem comes down to bad land use. BIBLIOGRAPHY http://www.gould.edu.au/foodwebs/afgrasslandsC.htm http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/african_savanna.htm http://www.conserveafrica.org.uk/nwfp.html http://www.traffic.org/dispatches/archives/january99/ The Times Atlas of the World, New Reference Edition, Times Books, London, 1999. Encyclopedia of Animals, Mammals and Birds, Fog City Press, U.S.A 2003. |